Press Brake Accuracy Inspection Guide
Table of Content
This post is also available in:
Español (Spanish) العربية (Arabic) Русский (Russian)
CNC Press Brake Accuracy Inspection – Testing of the Accuracy
According to (GB/T 33644-2017)
1 Scope This standard specifies the inspection requirements, allowable values and inspection methods for the accuracy of NC press brake. This standard is applicable to the NC press brake. 2 Normative references The following referenced document is indispensable for the application of this document.
1 Scope
This standard specifies the inspection requirements, allowable values and inspection methods for the accuracy of NC press brake.
This standard is applicable to the NC press brake.
2 Normative References
The following referenced document is indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition (including any amendments) applies.
GB/T 8170
GB/T 10923-2009
Rules of rounding off for numerical values & expression and judgment of limiting values Test code of accuracy for metal forming machine
3 CNC Press Brake Accuracy Inspection Requirements
3.1.1 The installed press brake shall be adjusted to be leveled before the inspection of accuracy, which shall not exceed 0.20/1,000 in the longitudinal and transverse directions.
3.1.2 The geometric accuracy and numerical control accuracy shall be inspected under the condition of no load.
3.1.3 The accuracy inspection shall be carried out after full load test.
3.1.4 During the accuracy inspection, the mechanism and parts affecting the accuracy shall not be adjusted.
3.1.5 The accuracy inspection and inspection gauge shall comply with GB/T10923.
3.1.5 The accuracy inspection and inspection gauge shall comply with GB/T10923.
3.1.6 When the actual measured length is less than the length specified in the tolerance clause, the accuracy shall be converted according to the actual measured length, and then rounded to micron digits according to GB/T 8170.
3.1.7 The limit deviation of specimen length and width is 2mm, and that of specimen thickness is 0.3mm.
3.1.8 For multi-motor synchronization NC press brake, the geometric accuracy and working accuracy are inspected on single machine respectively.
3.2 Working accuracy Inspection Conditions
3.2.1 The specimen length shall meet the requirements of Table1.
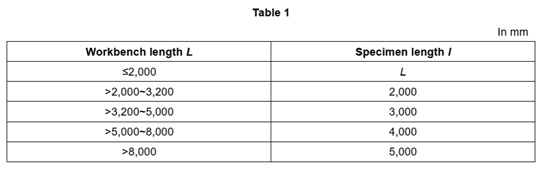
3.2.2 The specimen width shall be greater than 30 times of specimen thickness, but not less than 100mm.
3.2.3 The specimen thickness shall meet the requirements of Table 2.
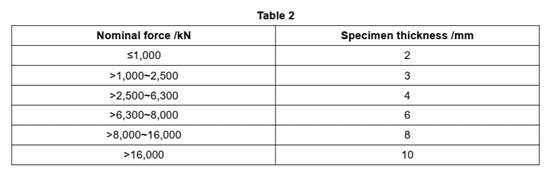
3.2.4 The specimen shall be made of Q235-A steel plate which has a tensile strength ofob450MPa.
3.2.5 The specimen quantity shall not be less than three.
3.2.6 The opening size of the lower die in the test is 8-10 times of the specimen thickness.
3.2.7 The specimen shall be placed in the middle of the workbench.
3.2.8 The specimen shall be bent by 90.
3.2.9 The measurement shall be started from 100mm away from the end of the specimen.
3.2.10 The thermal-cutting specimens shall be machined to remove the thermal stress affected zone.
4 CNC Press Brake Accuracy Inspection
4.1 Geometric accuracy
4.1.1 Flatness of workbench surface
4.1.1.1 Tolerance
4.1.1.1.1 The longitudinal tolerance in the flatness of workbench surface shall meet the requirements of Table 3.
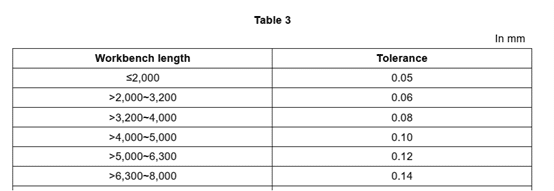
4.1.1.1.2 The transverse tolerance in the flatness of workbench surface shall meet the requirements of Table 4.
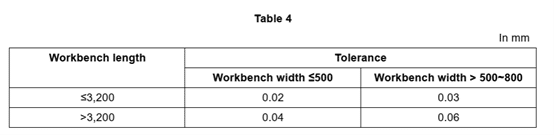
4.1.1.2 Inspection method
4.1.1.2.1 Longitudinal
According to GB/T10923-2009, 5.3.2.4.2, connect the gradient or optical instrument at a position 50mm from the end face of the workbench as shown in Figure1(the span of the gradienter may be between 100mm and 500mm) and place them on the workbench surface, take the readings in turn, and then determine the error value by graphic method (this item is not inspected for press brake with pre-convex or compensation devices on the workbench).
4.1.1.2.2 Transverse
According to GB/T 10923-2009, 5.3.2.4.2, place the gradienter or optical instrument on the workbench as shown in Figure2 for measurement and take the readings. There shall be no less than 3 measurements on the full length, and the error is calculated as the maximum difference between the readings (this item is not inspected for press brake with pre-convex or compensation devices on the workbench).
4.1.2 Parallelism of the horizontal bearing surface fitted to the upper die to the workbench surface
4.1.2.1 Tolerance
4.1.2.1.1 Longitudinal
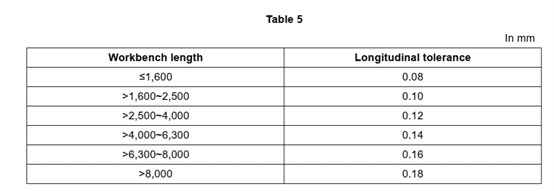
The longitudinal tolerance in the parallelism of the horizontal bearing surface fitted to the upper die to the workbench surface shall meet the requirements of Table 5.

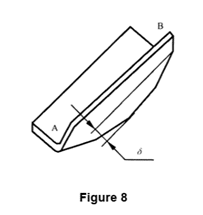
4.2.3 Double bending specimen
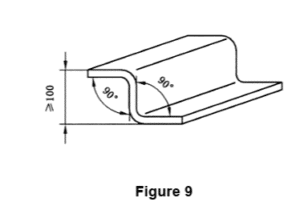
If the specimen material has a large stress difference, it is allowed to inspect the working accuracy by the specimen suffering from double bending (see Figure 9) and the inspection method shall comply with 4.2.1.2 and 4.2.2.2.

FAQ
What is the most accurate tool for measuring bend angles?
Digital angle gauges provide the highest accuracy. They display measurements in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Operators use these gauges to check angles quickly and reduce human error.
How often should operators calibrate a press brake?
Operators should calibrate every 500 operating hours or after changing tooling. Complex workpieces may require more frequent calibration. Keeping records helps track accuracy over time.
Why does material type affect CNC press brake accuracy?
Different metals have unique springback and yield strength. Aluminum bends more easily than steel. Operators must adjust settings for each material to maintain precise results.
Can environmental conditions impact measurement results?
Temperature changes cause metal expansion or contraction. High humidity can shorten tool lifespan. Operators monitor these factors to ensure consistent accuracy.
What should operators do if they notice inconsistent bends?
Operators should inspect tooling for wear, check machine alignment, and review calibration records. They may need to recalibrate or replace worn parts to restore accuracy.
