Servo Motor vs Induction Motor: 5 Key Differences for Your Hydraulic Press Brake
Table of Content
This post is also available in:
Español (Spanish) العربية (Arabic) Русский (Russian)
Servo Motor vs Induction Motor: 5 Key Differences That Affect Your Press Brake Machine Performance
In the world of hydraulic press brakes, the choice between servo motors and three-phase induction motors significantly impacts performance, efficiency, and cost. In this article, we will explore how these two types of motors compare, focusing on their features, working principles, and advantages when applied to servo-driven hydraulic press brakes.
Three-Phase Induction Motor: Simple but Limited
Three-phase induction motors are known for their simple design and reliable performance. These motors consist of two main components: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part that includes the supporting frame, stator core, and windings, while the rotor is the rotating part responsible for torque transmission.
Working Principle:
The three-phase induction motor operates based on electromagnetic induction. When a three-phase current flows through the stator windings, a rotating magnetic field is created, which induces a current in the rotor windings, generating torque. While this design offers simplicity and reliability, it has limitations, especially when it comes to speed control and precision.
In hydraulic press brakes, three-phase induction motors are often used for basic, high-power operations, but they lack the precision and control required for high-accuracy bending tasks. Additionally, they have issues with high inrush current at startup and energy inefficiency, making them less suitable for modern manufacturing needs.
Servo Motor: Precision and Efficiency for Hydraulic Press Brakes
In contrast, servo motors are more complex and precise, making them ideal for applications like hydraulic press brakes where high accuracy is required. A servo motor consists of the stator and rotor, along with additional components like feedback sensors to monitor and adjust the motor’s position and speed.
Working Principle:
A servo motor works by converting the input control voltage into precise speed and torque. Unlike induction motors, servo motors can provide closed-loop control, adjusting their behavior according to the actual output. This closed-loop system, combined with the motor’s encoder, allows for highly accurate control of speed and position, making it the perfect choice for precision-driven applications like hydraulic press brakes.
In hydraulic press brake applications, the servo motor ensures fine control over the bending process, resulting in high displacement accuracy and consistent repeatability. This is especially important in high-precision manufacturing where accuracy and energy savings are critical.
Performance and Features: Servo vs. Induction Motors
When comparing servo motors and three-phase induction motors for use in hydraulic press brakes, here are the key differences:
-
Three-Phase Induction Motor:
-
Simple and cost-effective
-
Reliable for high-power, less-precise applications
-
Limited speed control
-
Higher energy consumption and inefficiency
-
Higher inrush current at startup
-
-
Servo Motor:
-
Superior precision and closed-loop control
-
High efficiency, with reduced energy consumption
-
Wide speed regulation for adjustable bending
-
Reduced noise levels (7dB quieter than induction motors)
-
Higher upfront cost but superior long-term savings due to energy efficiency and minimal wear on components
-
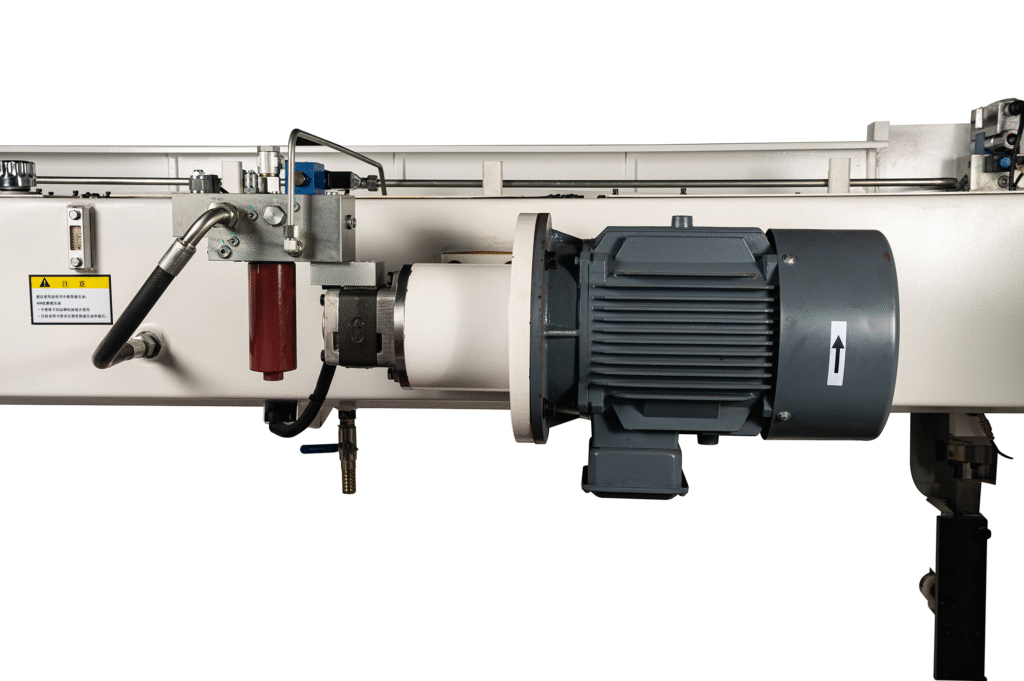
Meca Press Brake Equipped with ESTUN Servo Motor
Meca’s hydraulic press brake, equipped with the ESTUN servo motor, takes full advantage of the precision and efficiency that servo motors offer. The servo motor enables precise control of speed and flow, improving the adjustable operation of the machine. Under identical process conditions, productivity increases by 10% per unit time, and energy consumption is reduced by up to 50%. This energy savings is especially notable during idle periods, such as during workpiece repositioning.
In addition to the energy savings, the servo motor in Meca press brakes helps reduce noise levels by 7dB compared to traditional induction motors, enhancing the working environment. The servo motor also minimizes heat generation, leading to longer lifespan and reduced wear on hydraulic components.
Conclusion: Servo Motor vs Induction Motor, Which Motor is Right for Your Press Brake?
The choice between a servo motor and a three-phase induction motor for your hydraulic press brake ultimately depends on your specific needs:
-
For high precision, efficiency, and energy savings, servo motors are the clear choice. They provide closed-loop control, accurate positioning, and significant energy savings—ideal for industries requiring precise, consistent bending.
-
For simpler applications where cost-effectiveness and basic operational efficiency are more important, three-phase induction motors may be sufficient.
Boost Your Press Brake’s Performance with the Right Motor Choice
