Understanding the Complete Workflow of Hydraulic CNC Press Brake Machine Manufacturing
Table of Content
The complete workflow of hydraulic CNC press brakes covers a series of precise steps that shape the final machine. A hydraulic CNC press brake, manufactured by a leading Press brake manufacturer, uses advanced controls and hydraulic power to bend and form metal sheets, making it vital for modern manufacturing. These machines hold a strong position in the industry, with hydraulic press brakes expected to account for 46.8% of market revenue by 2025. Each stage in Press Brake Machine Manufacturing affects the final quality and performance. Industry studies show that the workflow improves accuracy, saves material, and allows for flexible production.
| Aspect | Impact on Quality and Performance |
|---|---|
| Precision | Enhances accuracy in metal bending operations |
| Efficiency | Reduces waste and human errors |
| Versatility | Adapts to various shaping needs |
Key Takeaways
- Hydraulic CNC press brakes are essential for precise metal bending, improving accuracy and reducing waste in manufacturing.
- Each step in the manufacturing process, from cutting to assembly, directly impacts the quality and performance of the final product.
- Regular maintenance, including daily checks and annual oil changes, can extend the lifespan of hydraulic CNC press brakes by 30% to 50%.
- Proper welding and machining are crucial for ensuring the strength and reliability of the machine, affecting its long-term performance.
- Investing in quality components and following strict calibration procedures enhances the efficiency and safety of hydraulic CNC press brakes.
What Is a Hydraulic CNC Press Brake?
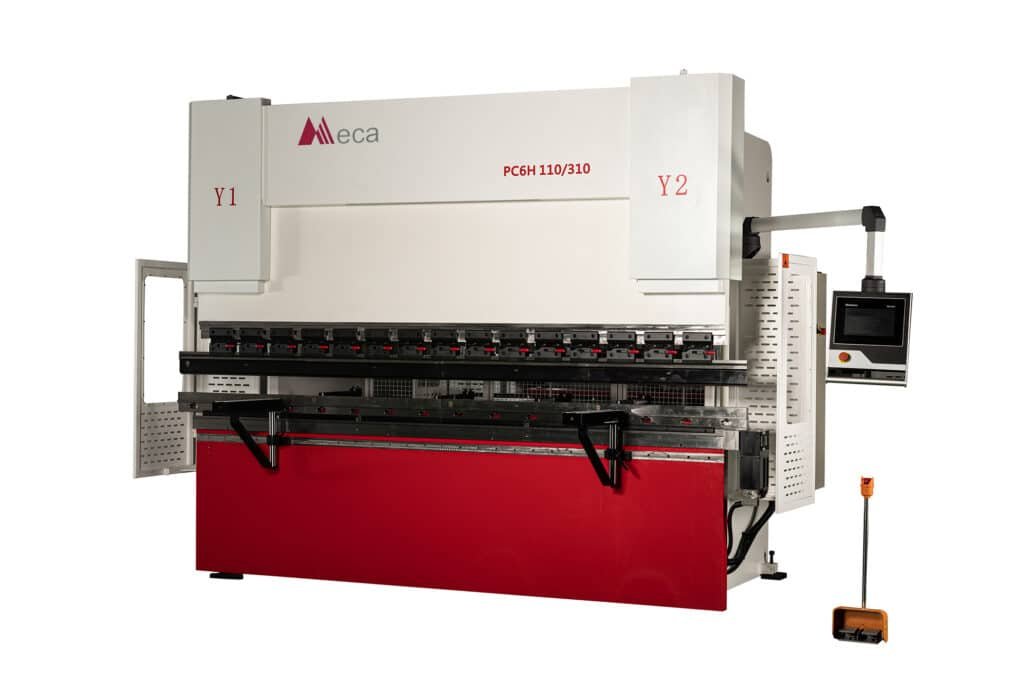

Definition
A hydraulic CNC press brake stands as a vital machine tool in modern metal fabrication. It uses hydraulic pressure to bend and shape metal sheets with high precision. The CNC (Computer Numerical Control) system automates the process, allowing operators to program complex bends and repeat them accurately. This technology supports industries that require consistent, high-quality metal parts.
The table below outlines the standard definition and features recognized by leading manufacturing organizations:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A hydraulic press brake is a machine tool that uses hydraulic pressure to deform material to a precise angle or shape. |
| Operation | It relies on the controlled movement and pressure of hydraulic fluid, resulting in smoother operation and superior control. |
| Features | Often equipped with multiple hydraulic cylinders for precise control, CNC systems for automation, and safety features for protection. |
Hydraulic CNC press brakes play a key role in Press Brake Machine Manufacturing, ensuring each product meets strict quality standards.
Main Parts
A hydraulic CNC press brake consists of several essential components. Each part works together to deliver accurate and reliable bending performance.
- Frame: Provides a stable base for the entire machine.
- Ram: Moves vertically to press the punch onto the workpiece over the die.
- Back Gauge: Positions the metal sheet for consistent and repeatable bends.
- Control Unit: Manages all operations, ensuring precise movements and settings.
- Hydraulic System: Powers the machine, including the motor, oil pump, oil filling valve, and oil cylinders.
- Hydraulic Pump: Converts mechanical energy into hydraulic power. Gear pumps handle low pressure, piston pumps manage high pressure, and vane pumps work with medium pressure.
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Transform hydraulic energy into mechanical force. Single-acting and double-acting types serve different applications.
These main parts form the foundation of every press brake, supporting the entire Press Brake Machine Manufacturing process.
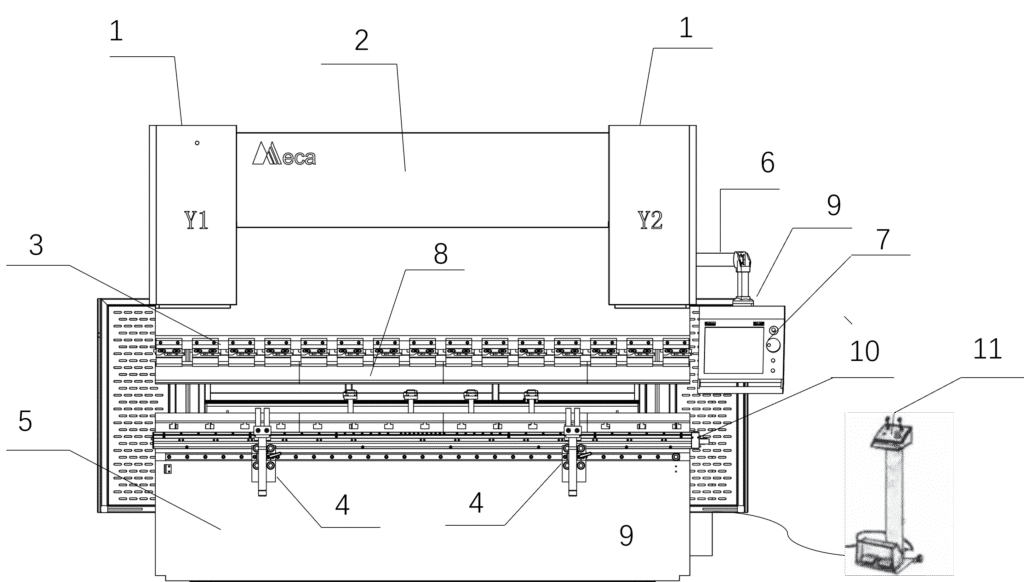
1.Y1, Y2 axis (oil cylinder)
2.Slider
3.Clamp
4.Front support
5.Working table
6.Hanger
7. Operation control panel
8.Toolings
9.Electric cabinet
10.Deflection compensation
11.foot pedal
Manufacturing Workflow of Hydraulic CNC Press Brakes—Press Brake Machine Manufacturing
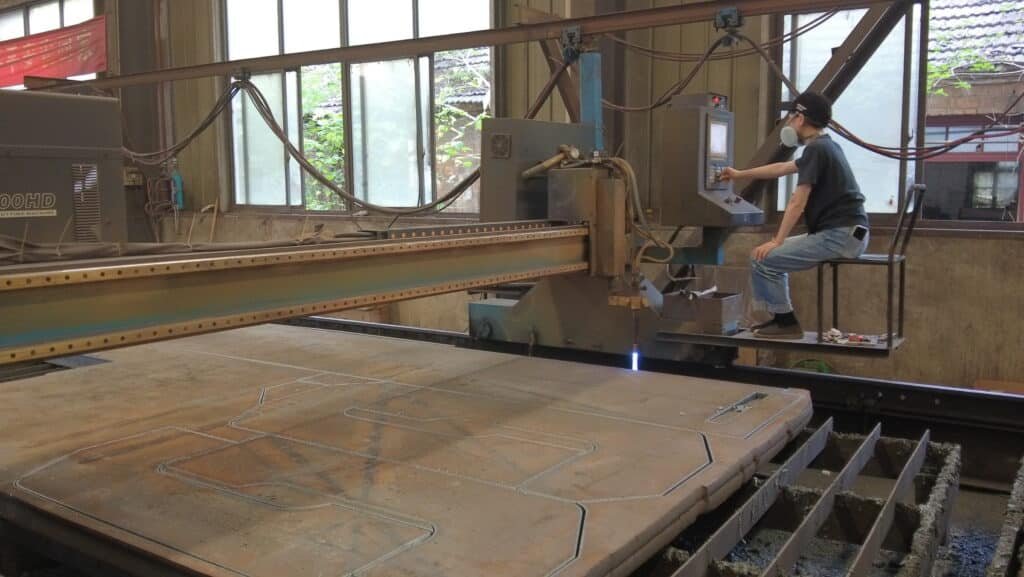
Steel Plate Cutting
Steel plate cutting marks the first step in Press Brake Machine Manufacturing. Workers select high-quality steel plates and cut them into precise shapes and sizes. This process uses advanced CNC machines to ensure accuracy. Tight tolerances are essential for critical alignments in the final machine. Operator skill plays a key role, especially when handling irregular shapes. The choice of cutting technique—such as Air Bending, Bottoming, or Coining—affects the final precision. Coining provides the tightest tolerances, making it ideal for demanding applications.

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Tolerances | CNC-controlled press brakes hold tight tolerances, essential for critical alignments. |
| Operator Skill | Skilled operators achieve high accuracy, especially for complex shapes. |
| Techniques | Air Bending, Bottoming, and Coining; Coining offers the highest precision. |
Accurate steel plate cutting lays a strong foundation for the entire Press Brake Machine Manufacturing process.
Borax Treatment
After cutting, the steel plates undergo borax treatment. Workers apply a borax solution to the metal surfaces. This step removes impurities and prevents oxidation during welding. Clean surfaces help create strong, reliable welds. Borax treatment also reduces the risk of defects in later stages. By preparing the steel properly, manufacturers ensure better performance and longer machine life.

Welding
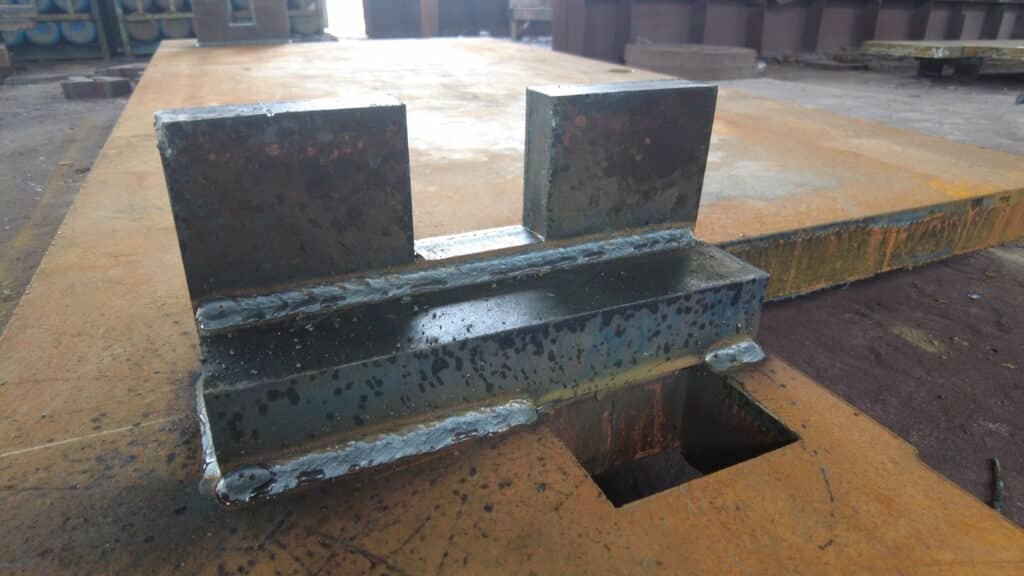
Welding joins the cut and treated steel plates into the main frame and other structural parts. Skilled welders use precise techniques to create strong, uniform joints. Proper welding ensures the frame can handle high pressure and repeated use. Any weakness in the welds could affect the safety and durability of the machine. In Press Brake Machine Manufacturing, welding quality directly impacts the machine’s reliability.

Machining
Machining shapes and finishes the welded components. Workers use lathes, milling machines, and grinders to achieve exact dimensions. Precision machining is critical for moving parts and alignment. Several advanced systems help maintain accuracy:
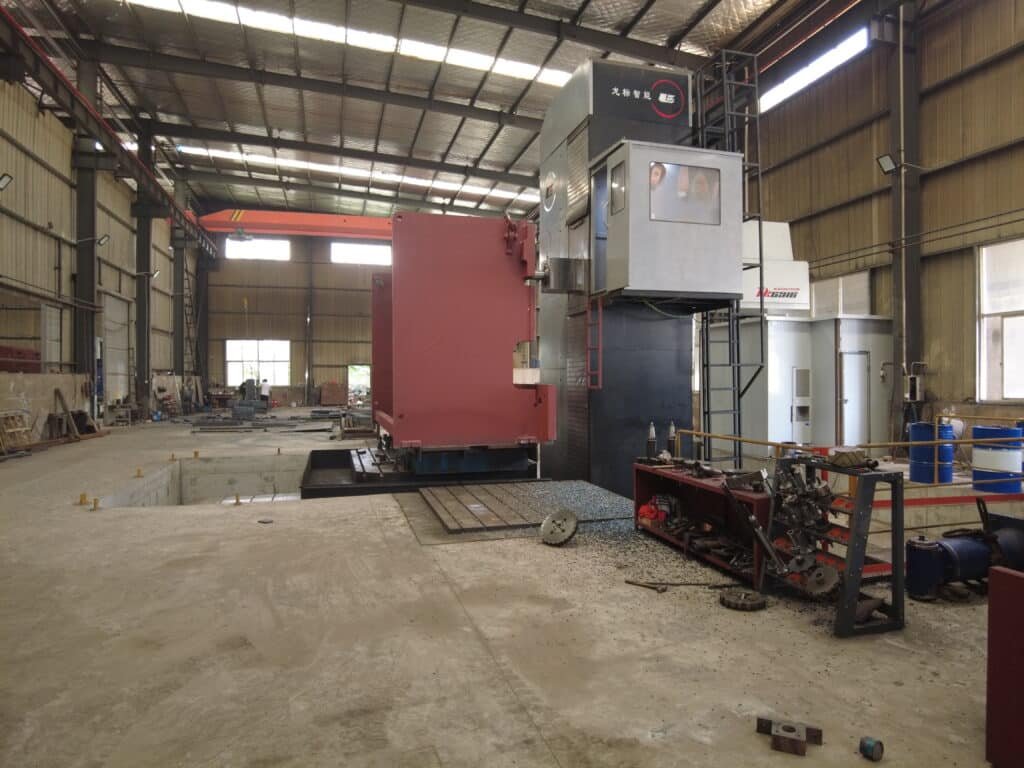

| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Servo Motors | Convert rotary motion into linear motion, ensuring high transmission efficiency and precision. |
| Linear Encoders | Provide continuous feedback on position, maintaining accuracy within ±0.02 mm. |
| Crowning Systems | Ensure straight bending, compensating for physical deformation during the process. |
| Automatic Deflection Comp. | Reduces angular deviation, improving first-pass success rates and minimizing material waste. |
To achieve optimal performance, manufacturers follow strict guidelines:
- Invest in a press brake with sufficient tonnage for the materials used.
- Maintain consistent ambient temperature to prevent thermal expansion.
- Implement regular calibration schedules for all measurement systems.
- Use certified materials with precise thickness tolerances.
- Train operators in precision techniques.
Machining ensures that every part fits perfectly, supporting the high standards of Press Brake Machine Manufacturing.
Painting
Painting protects the machine from rust, chemicals, and environmental damage. Workers apply several layers of specialized coatings. The process often starts with a zinc-rich primer for cathodic protection. An intermediate layer adds mechanical strength, while the topcoat resists UV damage and other environmental factors. Moisture-cured polyurethanes, such as Durabak, dry quickly and provide waterproof protection. These coatings remain flexible, so they do not crack when the machine moves.

| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Exceptional adhesion | Maintains protection despite constant movement. |
| Impact resistance | Prevents chipping and flaking. |
| Chemical resistance | Withstands exposure to oils and fluids. |
| UV stability | Prevents degradation from sun exposure. |
| Flexibility | Moves with the metal without cracking. |
| Self-healing properties | Maintains protection even after minor damage. |
Proper painting extends the life of the machine and keeps it looking new.
Assembly
Assembly brings together all the machined and painted parts. Workers fit the frame, hydraulic system, control unit, and other components with great care. Assembly accuracy determines how closely the final product matches design specifications. High accuracy reduces scrap rates and ensures that all parts fit together reliably. This step is essential for efficient manufacturing and long-term performance. Skilled operators, proper machine setup, and accurate programming all contribute to successful assembly.
Debugging
Debugging serves as the final step before the machine leaves the factory. Technicians check every component and test the machine’s performance. They inspect the hydraulic system, electrical connections, and control panel for correct installation. If they find any issues, they report them immediately for correction. Documentation and maintenance plans are prepared for the customer

Common issues identified during debugging include:
| Common Issue | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| No pressure in the hydraulic system | Solenoid coil issues, stuck cartridge valve, motor phase adjustment, damaged oil pump, blocked pressure control valve, etc. |
| Long pause time at speed change | Air in upper cavity, small flow rate, incomplete filling valve closure, low oil level, etc. |
| Ram not coming down in manual mode | Reversing valve issues, stuck filling valve |
A thorough debugging process ensures that each Press Brake Machine Manufacturing product meets strict quality standards and performs reliably in the field.
Testing & Quality
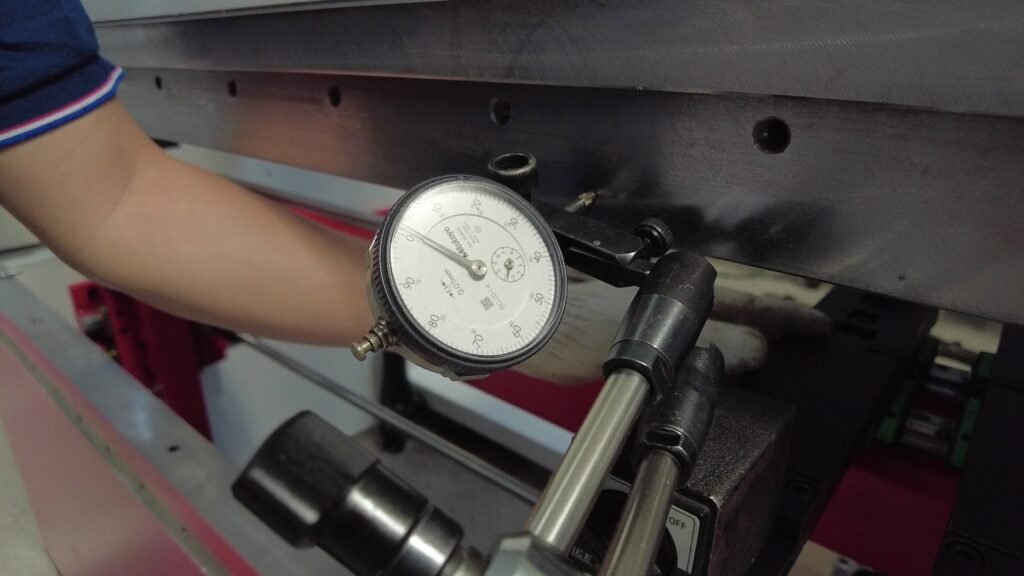

Calibration
Calibration ensures that hydraulic CNC press brakes deliver precise results in every operation. Technicians use several methods to verify accuracy. They check die holders for positioning and repeatability. The backgauge system undergoes calibration to match the CNC’s displayed coordinates with actual distances. Crowning compensation systems receive a three-section test to confirm consistent bend angles. Bend parameter calibration establishes a link between programmed angles and pressing depth. The table below summarizes these methods:
| Calibration Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Checking Die Holders | Verify positioning accuracy and repeatability of quick-clamp holders by measuring changes in critical surfaces. |
| Backgauge System Calibration | Ensure the CNC’s X-coordinate matches the physical distance from the gauge finger to the lower V-die center. |
| Crowning Compensation System Calibration | Perform a three-section test for consistent bend angles across the workpiece. |
| Bend Parameter Calibration | Use digital protractors and test dies to relate programmed angles to actual pressing depth. |
Technicians typically perform calibration once a year. For facilities that demand high productivity and accuracy, more frequent calibration may be necessary.
Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates how well the press brake meets operational standards. Technicians measure hydraulic system efficiency by monitoring pressure transducers and valve response times. They use digital angle finders to check bend angles against tolerances. Dial indicators verify parallelism and tool alignment. Sequential tests assess process consistency, including angle reproducibility and material springback. Cycle time measurements help optimize efficiency. The control system’s responsiveness and command execution latency also undergo assessment. The table below outlines key metrics:
| Metric Type | Evaluation Method |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic System Evaluation | Monitor pressure transducers for pump efficiency and valve response times. |
| Bend Angle Measurement | Use digital angle finders to measure angles and document variations. |
| Parallelism Verification | Mount dial indicators to check tool alignment and tolerances. |
| Process Consistency Analysis | Execute sequential tests for angle reproducibility and material springback. |
| Cycle Time Optimization | Measure complete bending cycle times for efficiency. |
| Control System Functionality | Assess CNC interface responsiveness and command execution latency. |
These tests confirm that each machine produced through Press Brake Machine Manufacturing meets strict quality requirements.
Final Inspection
Final inspection plays a vital role in ensuring reliability and safety. Technicians conduct regular inspections to maintain precision and safe operation. Early identification of issues guarantees that the CNC press brake operates efficiently. They always refer to the machine’s manual for specific procedures. Routine maintenance supports longevity and reliability. Preventive care reduces costly breakdowns and production delays. Technicians keep detailed logs of inspections and repairs to ensure accountability and trace recurring problems.
Tip: Consistent inspection and maintenance help extend the life of hydraulic CNC press brakes and improve workplace safety. 🛠️
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance keeps hydraulic CNC press brakes operating safely and efficiently. Technicians follow a schedule to inspect, clean, and lubricate key components. Regular care prevents breakdowns and extends machine life. The table below outlines recommended tasks and their frequency:
| Frequency | Maintenance Task |
|---|---|
| Daily | Turn off, lock out, and disconnect power to prevent accidents during maintenance. |
| Weekly | Lubricate moving parts, grease heavy components, oil delicate mechanisms, clean surfaces, and apply rust protectant. |
| Monthly | Inspect and tighten bolts and connections to address vibration-related issues. |
| Annually | Change hydraulic oil and filters, clean the tank, and install a new oil filter. |
| Regularly | Clean the hydraulic pump motor, inspect hydraulic circuits for leaks, and ensure secure connections. |
| Regularly | Wipe the touch screen with a microfiber cloth to remove oils and contaminants. |
Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of hydraulic CNC press brakes by 30% to 50%. Preventive programs achieve up to 85% equipment effectiveness, while post-failure repairs reach below 60%.
Common Issues
Operators sometimes encounter problems with hydraulic CNC press brakes. The most frequently reported issues include:
- Unresponsive controls, such as a CNC controller displaying random symbols.
- Pump not starting after initial operation.
- Complex wiring and control systems, especially after converting to shop power.
- Incorrect parameter entry, which affects machine function.
Troubleshooting these problems involves several steps:
- Check the voltage and power supply to the solenoid coil.
- Inspect the pressure control valve’s electrical signal.
- Examine cartridge valves and main spools for sticking or blockage.
- Confirm the oil pump’s rotation direction and condition.
- Verify the pressure gauge’s accuracy.
- Supply 24V electricity to test the valve oil pump.
- Adjust the compensation amplifier if pressure is limited.
- Look for air suction in the oil cylinder and inspect filling valves for proper operation.
Technicians also maintain the back gauge system by cleaning tracks, recalibrating through the control system, checking for wear, and reviewing software settings.
Tip: Consistent maintenance and prompt troubleshooting help prevent downtime and ensure safe, reliable operation. 🛠️
The manufacturing workflow of hydraulic CNC press brakes shapes both quality and safety. Each step, from steel cutting to final inspection, builds a foundation for reliable performance. Key features that enhance safety and reliability include:
- Programmatic tonnage protection halts the machine if force limits are exceeded.
- Collision simulation prevents accidental contact between parts.
- Tooling gap verification ensures correct installation.
- Smart integration with safety devices maximizes protection.
When evaluating a press brake, consider bending capacity, precision, energy efficiency, after-sales support, and machine stability. These factors help ensure long-term value and safe operation.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of hydraulic CNC press brakes?
Hydraulic CNC press brakes offer precise control and repeatability. Operators can program complex bends. The machine handles high workloads with consistent accuracy.
How often should technicians perform maintenance?
Technicians should follow a regular schedule. Daily checks, weekly lubrication, and annual oil changes help maintain safe and efficient operation.
Which industries use hydraulic CNC press brakes?
Manufacturers in automotive, aerospace, construction, and appliance production rely on hydraulic CNC press brakes. These machines shape metal parts for many products.
Why is borax treatment important in manufacturing?
Borax treatment cleans steel surfaces. It prevents oxidation and improves weld quality. Strong welds increase machine reliability.
Can operators troubleshoot common issues without advanced tools?
Operators can check power supply, inspect valves, and clean components. For complex problems, technicians may need specialized equipment.
Tip: Regular training helps operators identify and solve issues quickly. 🛠️
